Electric skateboards are revolutionizing the way we commute and have fun. But how do these sleek, speedy boards actually work? Let's dive into the mechanics and technology behind electric skateboards.
How Do Electric Skateboards Work?
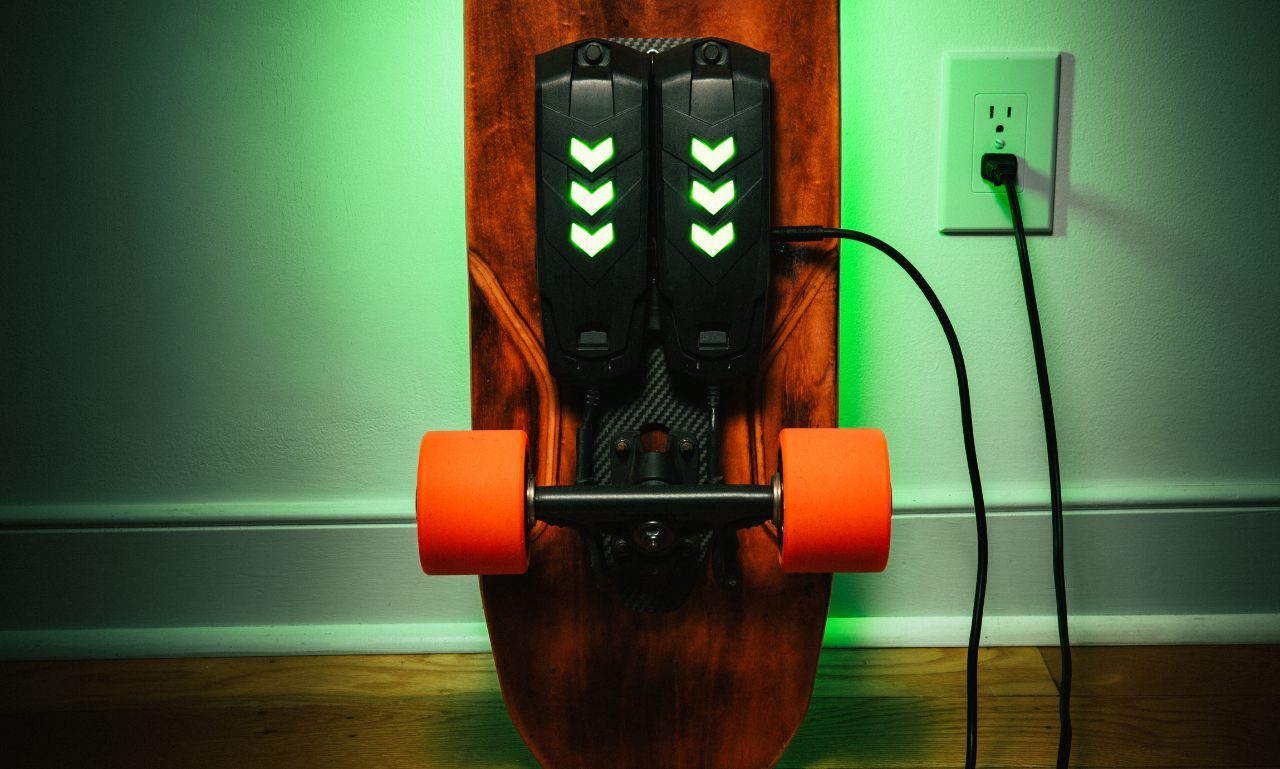

Electric skateboards work by converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy through the motors. Here's a step-by-step explanation:
- Power On: The rider powers on the skateboard and the remote control.
- Acceleration: Using the remote, the rider accelerates. The remote sends a signal to the electronic speed controller (ESC).
- Motor Activation: The ESC regulates the power from the battery to the motors.
- Movement: The motors turn the wheels, propelling the skateboard forward.
- Braking: The rider can also use the remote to brake, which engages the motors in reverse to slow down the board.
Key Components in Detail
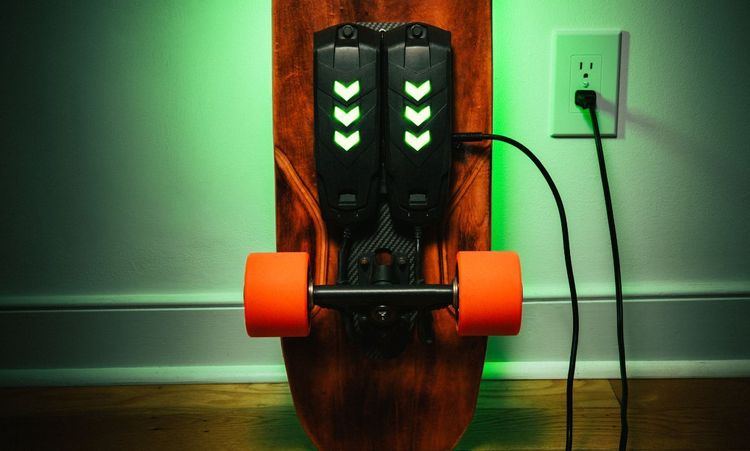
Electric skateboards are essentially traditional skateboards equipped with electric motors, batteries, and a remote control system. Here's a breakdown of the key components:
Deck
The deck is the foundation of the skateboard where the rider stands. It needs to be sturdy enough to support the rider's weight and the additional components. Common materials include:
- Maple Wood: Traditional and durable.
- Bamboo: Flexible and lightweight.
- Carbon Fiber: Extremely strong and lightweight, but more expensive.
Trucks
Trucks are crucial for steering and stability. They come in various sizes and materials, affecting the skateboard's performance.
Wheels

Electric skateboard wheels are designed for different terrains:
- Street Wheels: Smooth and hard, ideal for paved surfaces.
- All-Terrain Wheels: Larger and softer, suitable for rough terrains.
Motors
There are two main types of motors used in electric skateboards:
- Hub Motors: Integrated into the wheels, providing a sleek design and less maintenance.
- Belt-Driven Motors: Offer more torque and power, ideal for off-road and high-speed riding.
Battery
The battery is the powerhouse of the electric skateboard. Key factors include:
- Capacity: Measured in watt-hours (Wh), determines the range.
- Type: Lithium-ion batteries are common due to their high energy density and long lifespan.
Remote Control
The remote control is the rider's interface with the skateboard. It typically features:
- Throttle: For acceleration.
- Brake: For deceleration.
- Battery Indicator: Shows the remaining battery life.
Advanced Features
Modern electric skateboards come with advanced features such as:
- Regenerative Braking: Converts braking energy back into battery power.
- Smartphone Connectivity: Allows for firmware updates and performance tracking.
- Customizable Riding Modes: Adjusts speed and power settings for different skill levels.
Comparison Table
Feature
Hub Motors
Belt-Driven Motors
Design
Integrated into wheels
External, connected by belts
Maintenance
Low
Higher
Torque
Moderate
High
Noise
Quiet
Louder
Terrain Suitability
Best for smooth surfaces
Suitable for all terrains
Conclusion
Electric skateboards are a blend of traditional skateboarding and modern technology, offering a fun and efficient way to travel. By understanding the components and how they work together, you can make an informed decision when choosing your next ride.